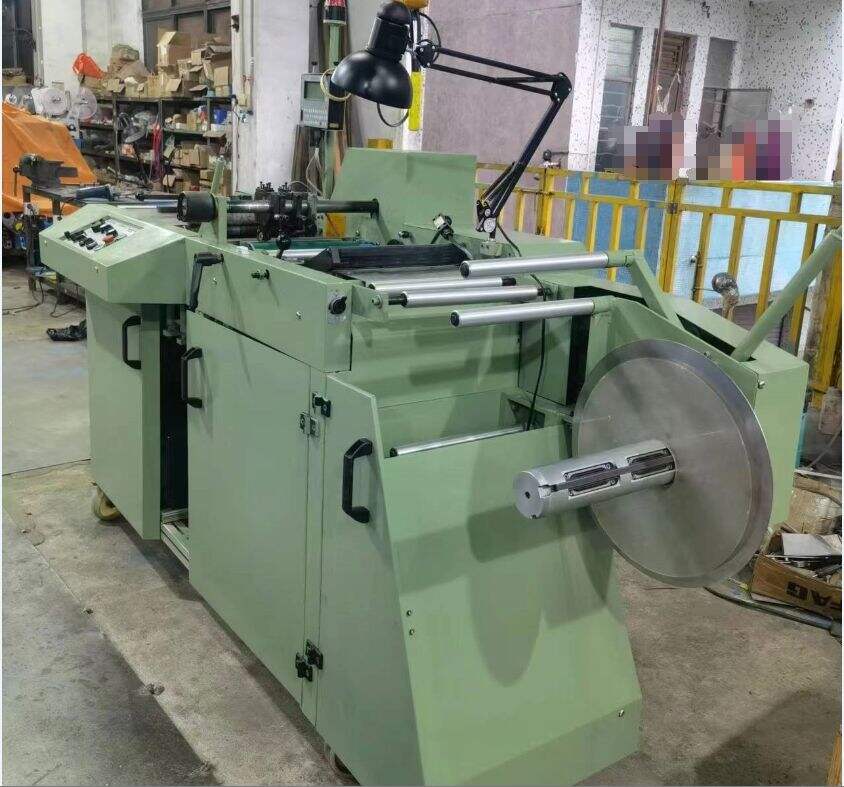
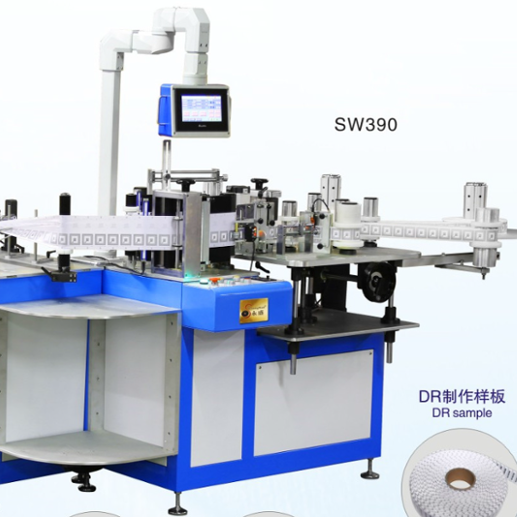
Akıllı Ürün Takibi İçin Neden RFID Kesme Mühür Makineleri Gerekli?
Modern envanter yönetimi ve ürün takip sistemleri, benzersiz bir hassasiyet ve verimlilik düzeyi gerektirir. Radyo frekansı tanımlama teknolojisinin otomatik mühürleme süreçleriyle entegrasyonu, işletmelerin tedarik zinciri görünürlüğüne ve ürün kimlik doğrulmasına yaklaşımını kökten değiştirmiştir. Bu teknolojik birleşme, doğru takip ve güvenli kimliklendirme işlemlerinin operasyonel başarı için büyük önem taşıdığı lojistik, imalat ve perakende sektörlerindeki kritik zorluklara çözüm sunar.
Akıllı takip sistemlerinin gelişimi, envanter kontrolü ve varlık yönetimi konusundaki geleneksel yaklaşımları temelden dönüştürmüştür. Çeşitli sektörlerdeki kuruluşlar, geleneksel barkod sistemleri ile manuel takip yöntemlerinin sınırlarını giderek daha fazla fark etmektedir. Bu eski yöntemler sıklıkla insan hatasına, zaman alıcı işlemlere ve tedarik zinciri boyunca yetersiz görünürlüğe neden olur. RFID destekli gelişmiş mühürleme teknolojilerinin ortaya çıkışı, bu tür operasyonel verimsizlikleri gidermede önemli bir ilerlemedir.
Günümüz işletmeleri, katı güvenlik standartlarını ve düzenleyici uyumu korurken operasyonlarını optimize etme yönünde artan bir baskı altındadır. Radyo frekansı tanımlama özellikli akıllı mühürleme mekanizmalarının entegrasyonu, aynı anda birden fazla operasyonel zorluğu ele alan kapsamlı bir çözüm sunar. Bu teknoloji, kuruluşların geliştirilmiş izlenebilirlik, artırılmış güvenlik ve iş hattını doğrudan etkileyen basitleştirilmiş iş akışı süreçlerine ulaşmasını sağlar ve bu da kârlılıklarını ve pazar içindeki rekabet konumlarını doğrudan etkiler.
RFID Mühürleme Sistemlerinin Temel Teknolojisi
Temel Bileşenler ve Mimarisi
RFID mühürleme sistemlerinin teknolojik altyapısı, güvenilir performans sunmak için uyum içinde çalışan birbirine bağlı birkaç bileşenden oluşur. Temel unsurlar arasında yüksek frekanslı radyo vericileri, özel anten dizileri, mikroişlemci kontrollü kesim mekanizmaları ve hassas mühürleme üniteleri yer alır. Bu bileşenler, zorlu endüstriyel koşullar altında daimi işlemeyi garanti eden sağlam bir yapı içinde entegre edilmiştir.
Gelişmiş mikrodenetleyici üniteler, RFID okuyucular ile mekanik mühürleme bileşenleri arasındaki iletişimi koordine eden merkezi işlem merkezi görevi görür. Sistem mimarisi, işletme hatalarını önlemek ve mühürleme süreci boyunca veri bütünlüğünü sağlamak amacıyla birden fazla emniyet mekanizması içerir. Gerçek zamanlı izleme özellikleri sayesinde operatörler, sistem performansını takip edebilir ve üretim süreçlerini etkileyebilecek olası sorunları erken aşamada tespit edebilir.
Bu sistemler için gereken hassas mühendislik, karmaşık kalibrasyon prosedürlerini ve kalite kontrol önlemlerini içerir. Sızdırmazlık kalitesinin ve RFID etiket yerleştirme doğruluğunun tutarlı olabilmesi için üretim toleranslarının son derece dar sınırlar içinde tutulması gerekir. Bu düzeydeki hassasiyet, sızdırmazlığı yapılan ürünlerin güvenilirliği ve ömürleri ile bunlara ilişkin izleme kabiliyetlerini doğrudan etkiler.
Radyo Frekansı Entegrasyon Prensipleri
Sızdırmazlık sistemlerinde radyo frekansı teknolojisinin uygulanması, elektromanyetik uyumluluk ve sinyal yayılım özelliklerinin dikkatli bir şekilde değerlendirilmesini gerektirir. Çalışma frekansları, okuma menzilini ve veri iletim güvenilirliğini en üst düzeye çıkarırken, çevredeki ekipmanlarla etkileşimi en aza indirecek şekilde seçilmelidir. Standart frekans aralıkları arasında düşük frekans, yüksek frekans ve ultra yüksek frekans bantları bulunur ve her biri belirli uygulamalar için farklı avantajlar sunar.
Sinyal gücü optimizasyonu, kapatma süreci boyunca tutarlı iletişim sağlamak üzere stratejik anten yerleştirme ve güç yönetim protokollerini içerir. Sistem, endüstriyel tesislerde tipik olan zorlu elektromanyetik ortamlarda bile güvenilir veri alışverişi sağlamalıdır. İleri sinyal işleme algoritmaları, iletişim güvenilirliğini artırır ve veri bozulması veya iletim hataları olasılığını azaltır.
Veri kodlama ve şifreleme özellikleri, güvenlik ve işlevsellik açısından ek katmanlar sağlar. Modern RFID kapatma sistemleri birden fazla veri formatını destekler ve belirli sektör gereksinimlerine göre uyarlanmış özel bilgi yapılarını barındırabilir. Bu esneklik, kuruluşların kapsamlı ürün bilgilerini, kimlik doğrulama kodlarını ve takip parametrelerini doğrudan kapatılmış paketin içine yerleştirmesine olanak tanır.
Sektörler Arası Stratejik Uygulamalar
İmalat ve Üretim Ortamları
İmalat tesisleri, kapsamlı ürün genealogisi ve kalite kontrol sistemleri oluşturmak için RFID mühürleme teknolojisinden yararlanır. Benzersiz tanımlayıcıları ve üretim parametrelerini doğrudan mühürlü paketlere yerleştirme yeteneği, üreticilerin üretim koşulları, kalite metrikleri ve uyum verileriyle ilgili ayrıntılı kayıtlar tutmalarını sağlar. Bu bilgi, düzenleyici denetimler, garanti talepleri ve sürekli iyileştirme girişimleri için çok değerlidir.
Üretim hattı entegrasyonu, mevcut ekipman ile yeni RFID mühürleme sistemleri arasında karmaşık bir koordinasyon gerektirir. Teknoloji, kurumsal kaynak planlama sistemleri, kalite yönetim veritabanları ve otomatik üretim kontrol sistemleriyle sorunsuz bir şekilde entegre edilmelidir. Bu entegrasyon düzeyi, takip bilgilerinin kuruluş boyunca sorunsuz bir şekilde akmasını sağlar ve veriye dayalı karar alma süreçlerini destekler.
Kalite güvence protokolleri, akıllı sızdırmazlık sistemlerinin uygulanmasından büyük ölçüde faydalanır. Otomatik doğrulama süreçleri, sızdırmazlık anormalliklerini tespit edebilir, RFID etiket işlevselliğini doğrulayabilir ve ürünler üretim hattını terk etmeden önce uygun veri kodlamasının yapılmasını sağlayabilir. Bu yetenekler, müşterilere ulaşan hatalı ürün olasılığını azaltır ve ürün geri çağırmaları veya garanti talepleriyle ilişkili maliyetleri en aza indirir.
Lojistik ve Dağıtım Ağları
Dağıtım merkezleri ve lojistik operasyonları, karmaşık tedarik zinciri ağlarında boyunca görünürlüğü ve kontrolü artırmak için RFID kesim mühürleme makineleri gerçek zamanlı sevkiyat takibi, otomatik envanter güncellemeleri ve büyük depo tesisleri içinde hassas konum belirleme imkanı sunar. Bu düzeydeki görünürlük, müşteri hizmetlerinin iyileştirilmesine, gönderim hatalarının azaltılmasına ve envanter doğruluğunun artırılmasına katkı sağlar.
Taşıma izleme özellikleri, taşıma koşulları, sıcaklık maruziyeti ve güvenlik durumu hakkında ayrıntılı bilgi sağlayarak geleneksel takip yöntemlerinin ötesine geçer. RFID sistemleriyle entegre edilmiş gelişmiş sensörler, yetkisiz erişim girişimlerini, çevresel değişiklikleri ve taşınma sırasında meydana gelen fiziksel hasarları tespit edebilir. Bu bilgiler, proaktif müdahaleye olanak tanır ve dağıtım süreci boyunca ürün bütünlüğünün korunmasına yardımcı olur.
Çapraz sevkiyat operasyonları, RFID destekli süreçlerin hızından ve doğruluklarından faydalanır. Gelen sevkiyatlar, gömülü takip bilgilerine göre otomatik olarak sıralanabilir ve yönlendirilebilir; bu da manuel işleme gereksinimini azaltır ve işlem gecikmelerini en aza indirir. Bu teknoloji, yüksek düzeyde doğruluk ve izlenebilirliği korurken hızlı bir dönüşüm sağlar.
Operasyonel Faydalar ve Performans Avantajları
Gelişmiş Güvenlik ve Kimlik Doğrulama
RFID mühürleme sistemlerinin sağladığı güvenlik geliştirmeleri, ürün manipülasyonu, sahtecilik ve yetkisiz erişim konularında artan endişelere çözüm sunar. Fiziksel mühürleme mekanizmaları ile elektronik kimlik doğrulamanın birleşimi, tespit edilmeden aşılması zor olan çok katmanlı bir koruma oluşturur. Açılma izi bırakma özellikleri, yetkisiz erişim girişimlerini anında görsel olarak belli eder.
RFID etiketlerine yerleştirilmiş kriptografik kimlik doğrulama protokolleri, sahte ürünlerin veya yetkisiz değişikliklerin tespit edilmesini sağlayan gelişmiş doğrulama süreçlerine imkan tanır. Bu güvenlik önlemleri, ürün orijinalliğinin doğrudan tüketici güvenliğini ve marka itibarını etkilediği ilaç, elektronik ve lüks eşya gibi sektörlerde özellikle önemlidir.
Erişim kontrolü özellikleri, organizasyonların mühürlü ürünlere ilişkin işlem izinlerini kısıtlamasına ve bireysel kullanıcı etkileşimlerini izlemesine olanak tanır. Bu düzeyde sorumluluk, uyum gereksinimlerini destekler ve düzenleyici raporlamalar için ayrıntılı denetim kayıtları sağlar. Sistem, yetkisiz erişim girişimleri tespit edildiğinde uyarı oluşturabilir ve potansiyel güvenlik ihlallerine hızlı müdahale edilmesini sağlar.
İşlem Verimliliği ve Maliyet Azaltma
Operasyonel verimlilikteki iyileşmeler, daha önce elle yapılan işlemlerin otomasyonu ve takip ile tanımlama görevlerinde insan hatasının ortadan kaldırılması sonucu meydana gelir. RFID mühürleme makineleri saatte yüzlerce birimi tutarlı doğrulukla işleyebilir ve manuel mühürleme ve etiketleme işlemlerinin performansını önemli ölçüde geçer. Bu verimlilik kazancı, organizasyonların iş hacimlerini artırırken iş gücü maliyetlerinde buna orantılı artış olmadan yönetmelerini mümkün kılar.
İşgücü maliyetlerinin azaltılması, manuel envanter sayımı, paket denetimi ve veri girişi faaliyetlerine olan ihtiyacın azalmasından kaynaklanır. Otomatik sistemler, bu görevleri yorgunluk veya dikkat dağıtım olmadan sürekli olarak gerçekleştirebilir ve uzun çalışma süreleri boyunca tutarlı bir performans sağlar. El işleme azaltılması, işyerindeki yaralanma riskini ve ilgili tazminat maliyetlerini de en aza indirmektedir.
Hata azaltma yetenekleri, düşen getiri, müşterilerin memnuniyetinin artması ve düşük idari genel masraflar yoluyla doğrudan maliyet tasarrufu ile çevrilir. Yanlış tanımlanan ürünlerin, yanlış sevkiyatların ve stok tutarsızlıklarının ortadan kaldırılması, operasyonel kârların iyileştirilmesine ve pazarda daha iyi bir üne katkıda bulunur.
Uygulama Konuları ve En İyi Uygulama Yöntemleri
Sistem Entegrasyonu ve Uyumluluk
RFID mühürleme sistemlerinin başarılı bir şekilde uygulanması, mevcut altyapı ve uyumluluk gereksinimlerinin dikkatli bir şekilde değerlendirilmesini gerektirir. Kuruluşlar, sorunsuz entegrasyonu sağlamak için mevcut kurumsal sistemlerini, ağ yeteneklerini ve operasyonel prosedürlerini değerlendirmelidir. Bu değerlendirme, veri akışı gereksinimlerini, sistem arayüzlerini ve performans beklentilerini de içermektedir.
Uyumluluk testi, tüm entegre sistemlerdeki iletişim protokollerinin, veri biçimlerinin ve operasyonel prosedürlerin doğrulanmasını içerir. Test aşamasında gerçek çalışma koşulları simüle edilmeli ve en yüksek yük koşullarında güvenilir performans sağlamak için stres testleri dahil edilmelidir. Entegre işlemleri ve sorun giderme protokollerinin kapsamlı belgelendirilmesi, devam eden bakım ve sistem optimizasyonu çabalarını destekler.
Eğitim gereksinimleri, yeni teknolojinin hem teknik hem de operasyonel yönlerini kapsar. Personel, optimal performansı sağlamak için sistem yeteneklerini, bakım prosedürlerini ve sorun giderme tekniklerini anlamalıdır. Devam eden eğitim programları, yatırımın geri dönüşünü en üst düzeye çıkarmak için sistem güncellemelerini, yeni özellikleri ve gelişen en iyi uygulamaları ele almalıdır.
Performans İyileştirme Stratejileri
Performans optimizasyonu, sistem ölçümlerinin sürekli izlenmesini ve operasyonel parametrelerin sistematik olarak iyileştirilmesini içerir. Ana performans göstergeleri, işlem oranları, hata oranları, bakım gereksinimleri ve kullanıcı memnuniyeti seviyelerini içermelidir. Bu ölçümlerin düzenli olarak analizi, optimizasyon fırsatlarının belirlenmesini ve potansiyel sorunların proaktif bir şekilde ele alınmasını sağlar.
Önleyici bakım programları, sistem performansının tutarlılığını korumak ve ekipman ömrünü uzatmak için gereklidir. Bu programlar düzenli kalibrasyon prosedürlerini, bileşen denetimlerini ve yazılım güncellemelerini içermelidir. Sensör verilerini ve performans analizini kullanan öngörüsel bakım teknikleri, operasyonları etkilemeden önce potansiyel arızaları belirlemeye yardımcı olabilir.
Sürekli iyileştirme girişimleri iş akışı süreçlerinin optimize edilmesine, sistem yeteneklerinin geliştirilmesine ve teknolojik ilerlemelerin dahil edilmesine odaklanmalıdır. İşletim prosedürlerinin ve sistem performansının düzenli olarak gözden geçirilmesi, verimlilik kazanımları ve maliyet azaltımları için fırsatları belirleyebilir. Teknoloji satıcılarıyla işbirliği, en son gelişmelere ve yükseltme seçeneklerine erişimi sağlar.
Gelecekteki Eğilimler ve Teknolojik Gelişme
Yeni Gelişen Teknolojiler ve Yenilikler
RFID mühürleme teknolojisinin evrimi yapay zekâ, makine öğrenimi ve gelişmiş sensör teknolojilerinin entegrasyonu ile ilerlemeye devam ediyor. Bu yenilikler sistem yeteneklerini artırmayı, öngörüsel bakımı iyileştirmeyi ve daha sofistike veri analizini mümkün kılmayı vaat ediyor. Makine öğrenimi algoritmaları, tarihsel performans verilerine ve çevresel koşullara dayanarak mühürleme parametrelerini optimize edebilir.
Nesnelerin İnterneti bağlantısı, uzaktan izleme, bulut tabanlı veri depolaması ve gelişmiş analitik sağlayarak RFID mühürleme sistemlerinin yeteneklerini genişletir. Bu bağlantı, küresel tedarik zincirleri boyunca gerçek zamanlı görünürlüğü destekler ve eğilimleri belirleyebilen ve operasyonları optimize edebilen öngörü analizini sağlar. Bulut entegrasyonu ayrıca daha kolay sistem güncellemelerini ve artan ölçeklenebilirliği kolaylaştırır.
Sürdürülebilirlik düşünceleri çevre dostu mühürleme malzemelerinin ve enerji verimli sistem tasarımlarının geliştirilmesini yönlendiriyor. Yeni biyolojik olarak ayrıştırılabilir mühürleme bileşikleri ve geri dönüştürülebilir RFID etiketleri, performans standartlarını korurken artan çevresel endişeleri ele alıyor. Enerji toplama teknolojileri, pil değiştirme gereksinimlerini ortadan kaldıran kendi kendine çalışan RFID etiketlerini sağlayabilir.
Pazar Gelişim ve Kullanım Eğilimleri
RFID mühürleme teknolojisinin piyasa kabulü, kuruluşların gelişmiş izleme ve güvenlik yeteneklerinin rekabet avantajlarını fark ettikleri için çeşitli endüstrilerde hızlanmaya devam ediyor. RFID teknolojisindeki maliyet azaltmaları ve sistem güvenilirliğinin iyileştirilmesi, küçük ve orta ölçekli işletmeler arasında daha geniş bir şekilde benimsenmesine neden oluyor. Sağlık, havacılık ve gıda işleme gibi sektörlerde benzersiz gereksinimleri karşılamak için endüstri özel çözümler ortaya çıkıyor.
Tedarik zincirinin şeffaflığı, ürün kimliği ve çevresel uyumluluk gibi alanlarda düzenleyici gelişmeler, karmaşık izleme ve mühürleme çözümlerine ek talep yaratıyor. Kuruluşlar, operasyonel verimliliği ve maliyet etkinliğini korurken değişen gereksinimlere uyum sağlamalıdır. RFID mühürleme sistemleri, bu değişen düzenleyici ortamlara cevap vermek için gereken esnekliği ve yetenekleri sağlar.
Küresel tedarik zincirinin karmaşıklığı artmaya devam ediyor ve kapsamlı izleme ve görünürlük çözümlerine daha fazla talep yaratıyor. RFID kesme mühürleme makineleri, kuruluşların kesintilere hızlı bir şekilde yanıt vermesini ve müşteri memnuniyetini korumasını sağlayan uçtan uca tedarik zinciri şeffaflığının temelini oluşturur. Teknoloji, daha esnek ve uyumlu tedarik zinciri stratejilerine yönelik eğilimleri desteklemektedir.
SSS
Geleneksel mühürleme yöntemlerine göre RFID kesme mühürleme makinelerinin temel avantajları nelerdir?
RFID kesme mühürleme makineleri, otomatik kimlik belirleme, geliştirilmiş güvenlik özellikleri ve tedarik zinciri boyunca iyileştirilmiş izlenebilirlik gibi önemli avantajlar sunar. Geleneksel yöntemlerin aksine, bu sistemler manuel veri girişi hatalarını ortadan kaldırır, tahrip edilemez güvenlik sağlar ve gerçek zamanlı izleme yeteneklerini sağlar. RFID teknolojisi ile kesme ve mühürleme işlemlerinin entegrasyonu, yüksek doğruluk seviyelerini korurken süreçleri kolaylaştırır ve işgücü gereksinimlerini azaltır.
RFID kesme mühür makineleri mevcut kurumsal sistemlerle nasıl entegre olur?
Entegrasyon genellikle mevcut kurumsal kaynak planlaması, depo yönetimi ve envanter kontrol sistemleriyle bağlantı kuran standartlaştırılmış iletişim protokolleri ve uygulama programlama arayüzleri aracılığıyla gerçekleşir. Makineler gerçek zamanlı olarak veri gönderebilir, envanter kayıtlarını otomatik olarak güncelleyebilir ve önceden tanımlanmış iş kurallarına dayalı iş akışı süreçlerini tetikleyebilir. Ortak veritabanı formatları ve ağ protokolleriyle uyumluluk, kuruluş boyunca sorunsuz veri akışını sağlar.
RFID mühürleme ekipmanlarıyla ilgili bakım gereksinimleri nelerdir?
Düzenli bakım, kesme mekanizmalarının kalibrasyonunu, RFID antenlerinin temizlenmesini ve mühür kalite parametrelerinin doğrulanmasını içerir. Önleyici bakım programları genellikle günlük operasyonel kontrolleri, haftalık performans değerlendirmelerini ve aylık kapsamlı incelemeleri içerir. Yazılım güncellemeleri ve sistem tanılamaları, optimal performansı sağlamak ve gelişen teknoloji standartlarıyla uyumluluğu korumak için düzenli olarak yapılmalıdır.
RFID kesme mühür makinesi teknolojisinin uygulanmasından en çok hangi sektörler faydalanır
Yüksek değerli ürünler, katı düzenleyici gereklilikler veya karmaşık tedarik zincirleri bulunan sektörler bu teknolojiden en büyük ölçüde faydalanır. İlaç şirketleri, uyum takibi ve sahtecilik önleme önlemleri için bu sistemleri kullanır. Elektronik üreticiler, garanti yönetimi ve kalite kontrolü için bu teknolojiyi kullanır. Lojistik şirketleri ise sevkiyat görünürlüğünü artırmak ve dağıtım ağlarında taşıma hatalarını azaltmak amacıyla bu sistemleri uygular.
Önerilen Ürünler
Son Haberler
-
Bilginin korunması ve yayılması için baskı matbaasının kültürel önemini düşünün
2023-12-08
-
Dünya ekonomisinde baskı matbaasının rolü
2023-12-08
-
Çevreye etkisi: baskı endüstrisinin çevresel ayak izini analiz etmek
2023-12-08
-
Baskı sınırları: 3D baskı ve endüstriyel direnişi
2023-12-08
-
Baskı matbaasının gelişimi ve etkisi
2023-12-08

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 VI
VI
 SQ
SQ
 HU
HU
 MT
MT
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 AF
AF
 GA
GA
 BN
BN
 BS
BS
 LO
LO
 LA
LA
 MI
MI
 MN
MN
 NE
NE
 MY
MY
 KK
KK
 UZ
UZ
 KY
KY









